Scroll for prep

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.
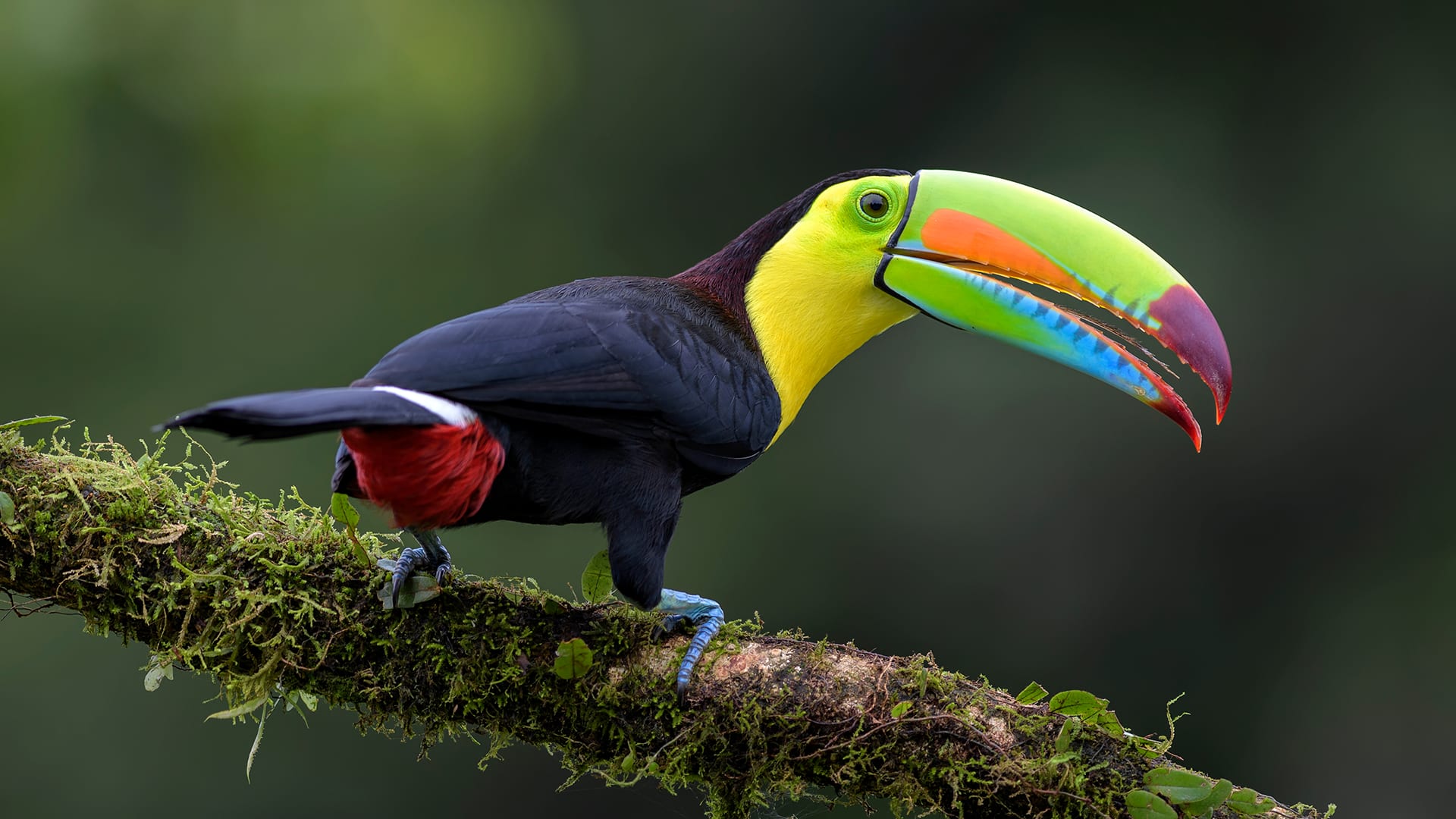
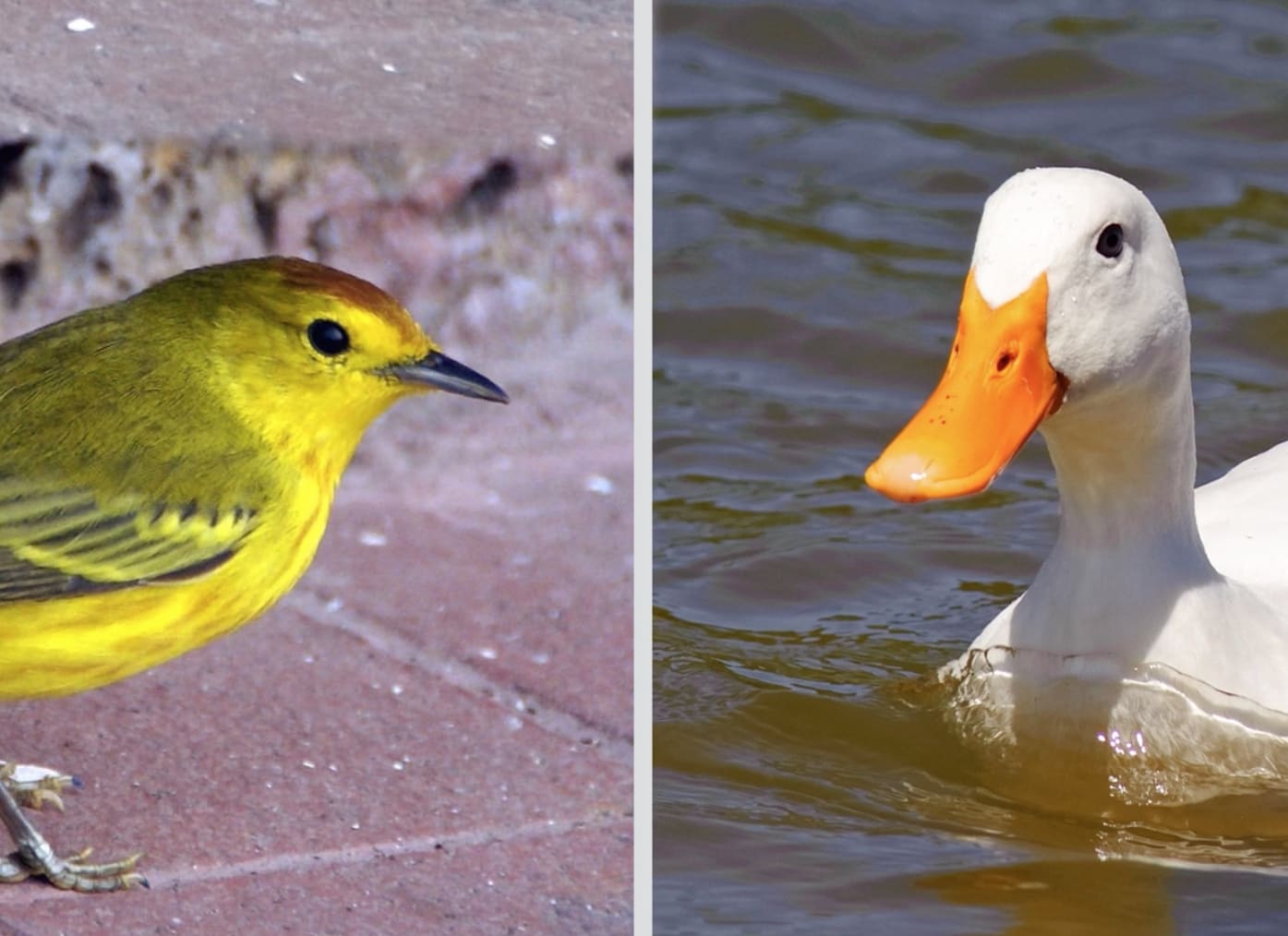
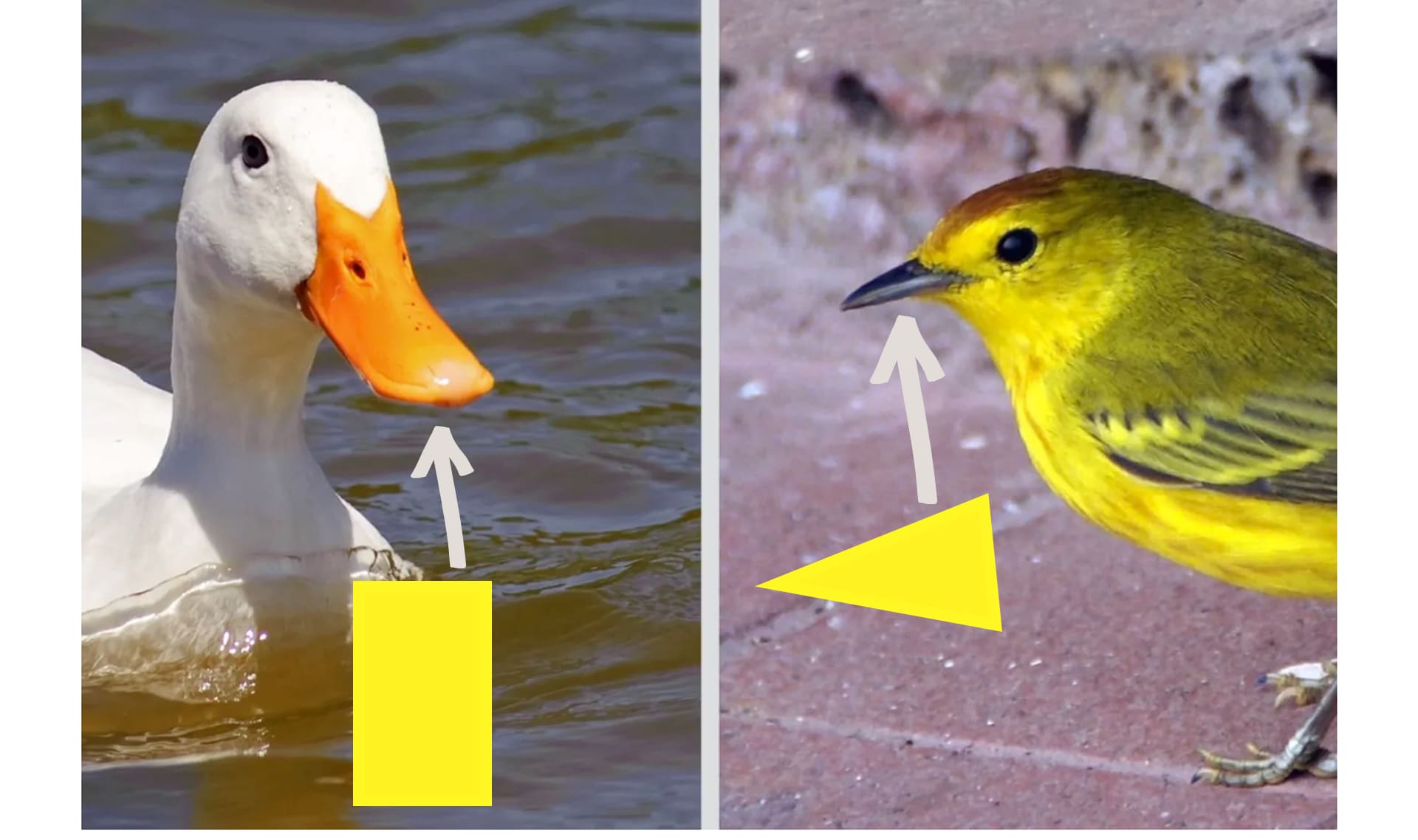
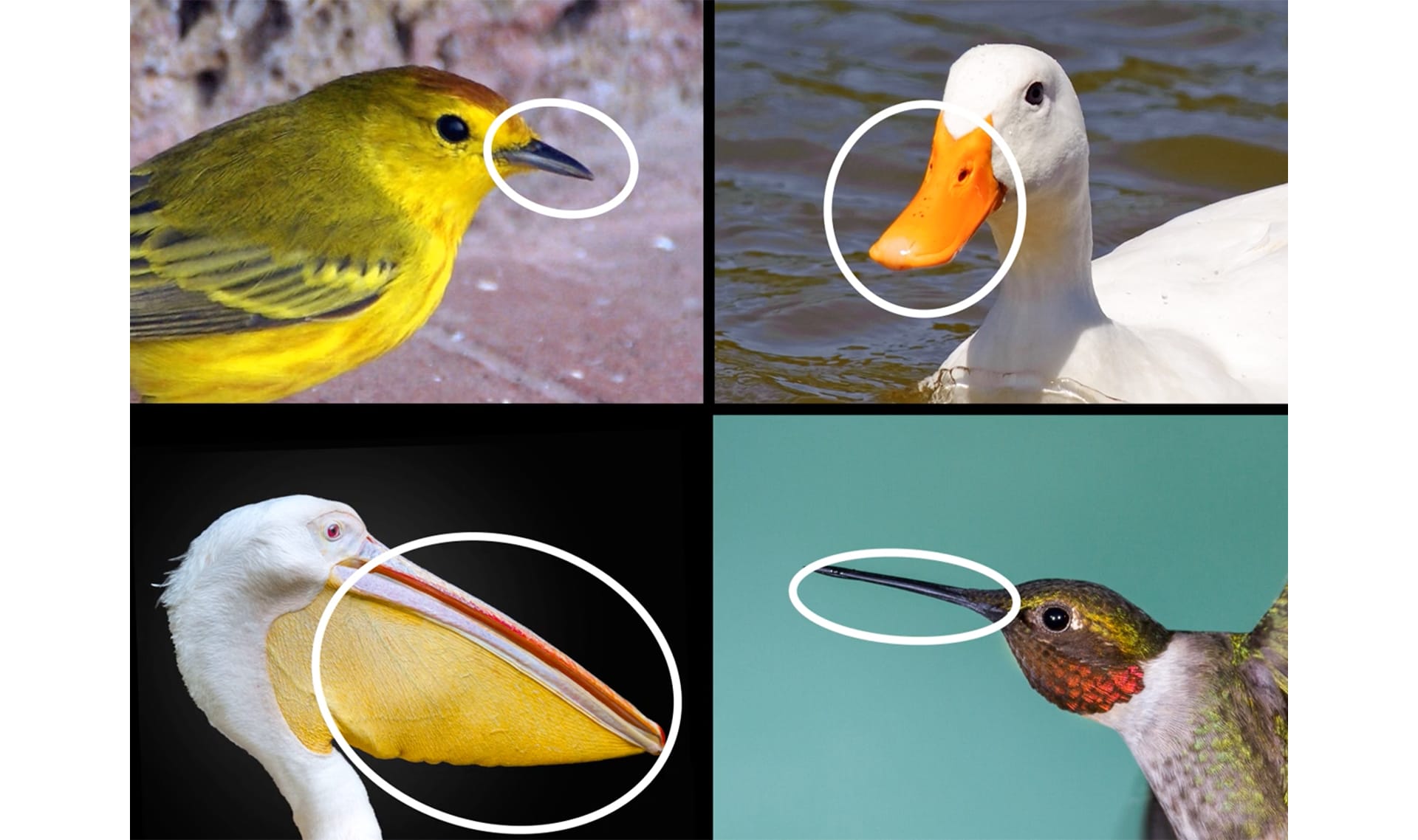
DISCUSS: How are these beaks different?


Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.
Thinking Activity (Part 1)
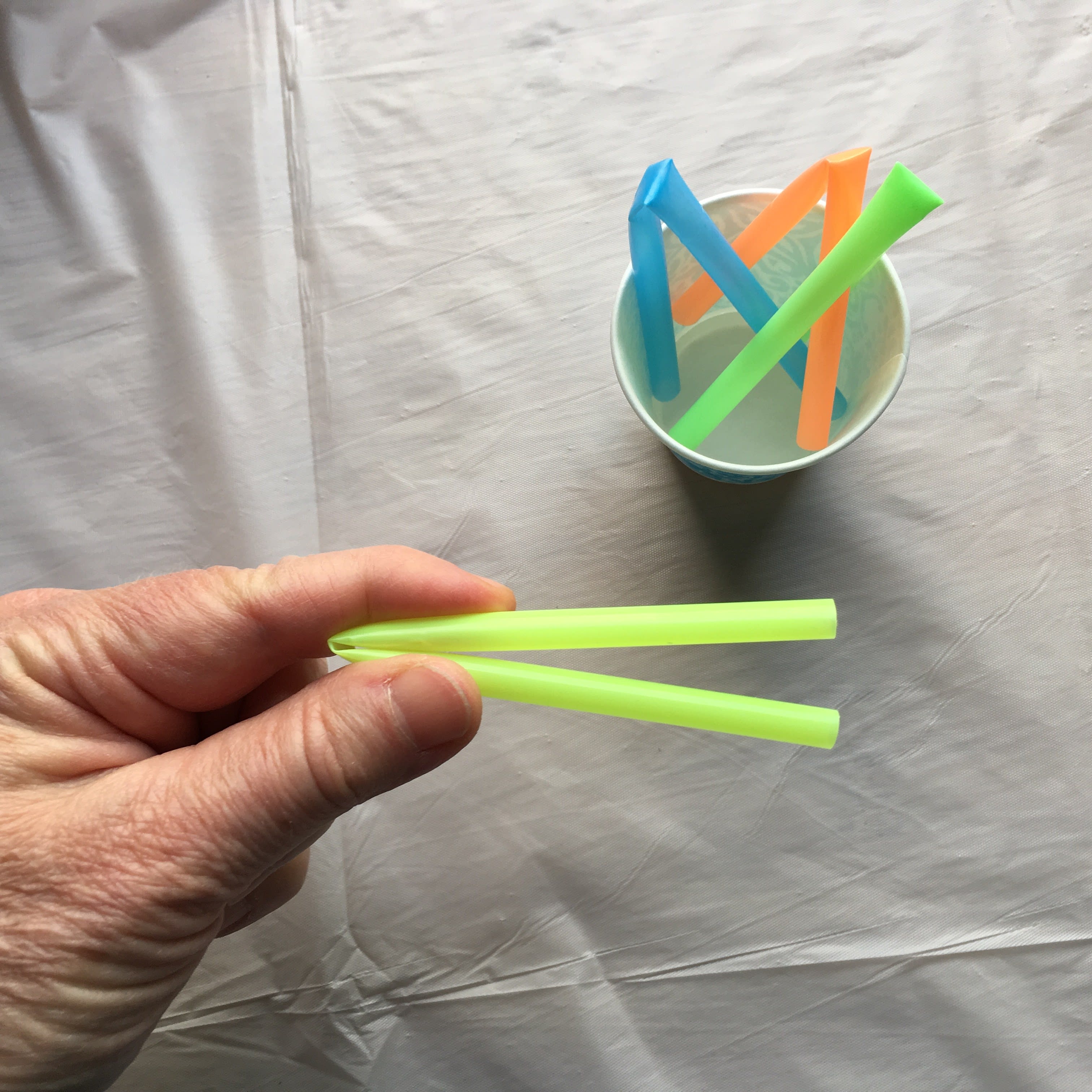
A bird’s beak is like a tool that helps the bird eat. What kinds of tools would you use if you wanted to:
- Crack a nut open?
- Scoop cereal out of a bowl filled with cereal and milk?
- Sip soda from a tall glass?
- Catch a slippery fish?
Can you think of a bird beak that works like these tools?
If you’re stumped, advance to the next slide to see our ideas.
Thinking Activity (Part 2)
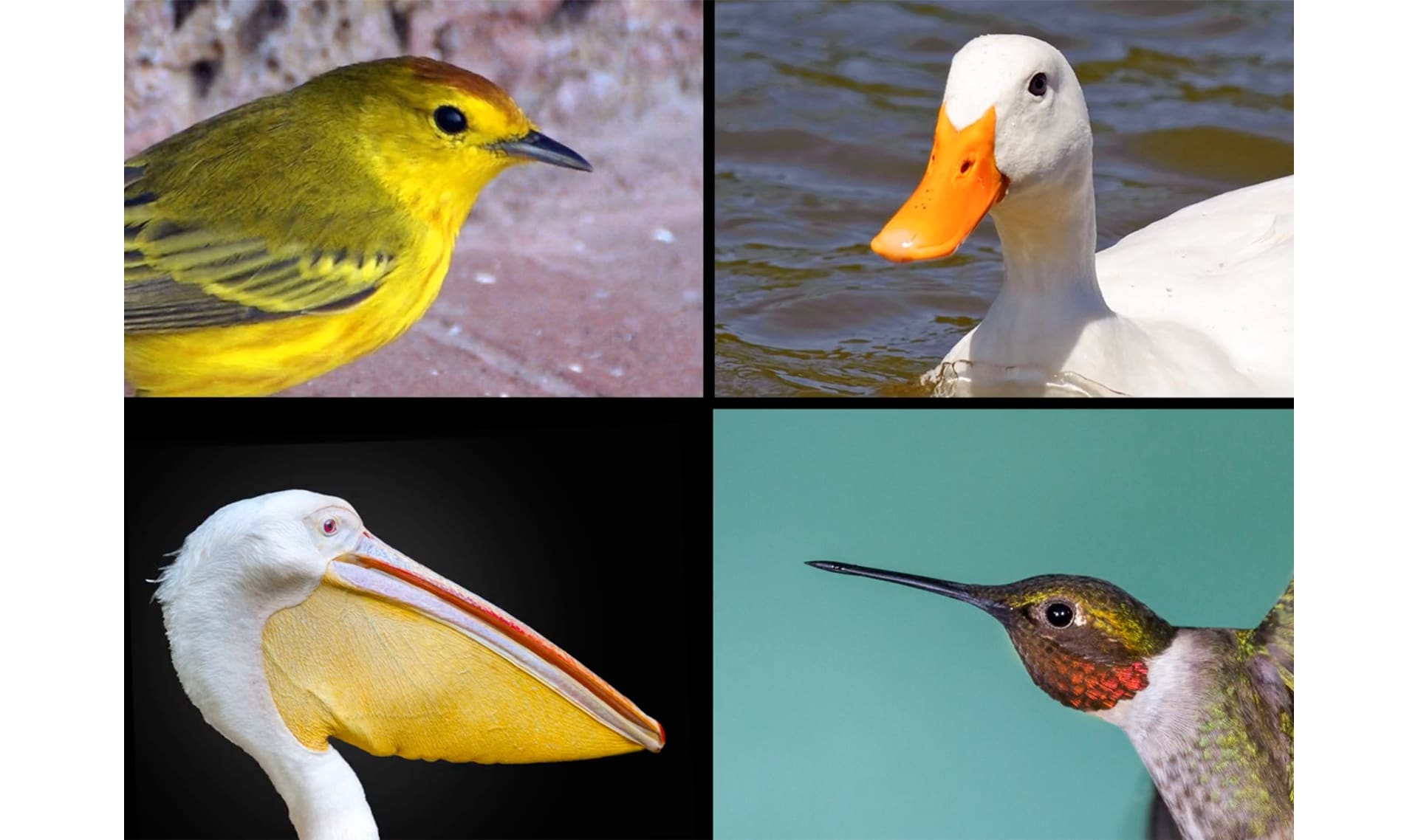
At Mystery Science, we use nutcrackers for cracking nuts. A parrot’s beak is short and strong, and it works like a nut cracker.
A spoon is good for scooping up soggy cereal. It works like a duck’s broad bill.
A straw helps you sip soda from the bottom of a tall glass, just like the hummingbird’s beak lets that bird sip the sweet juice called nectar from the bottom of a flower.
A fork can stab a slippery fish, just like the pointy beak of an egret.

shape
1 of 13
how something looks, such as circle, square, or triangle

size
2 of 13
how big or small something is

structure
3 of 13
the specific form and shape of something

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.
function
4 of 13
what something does
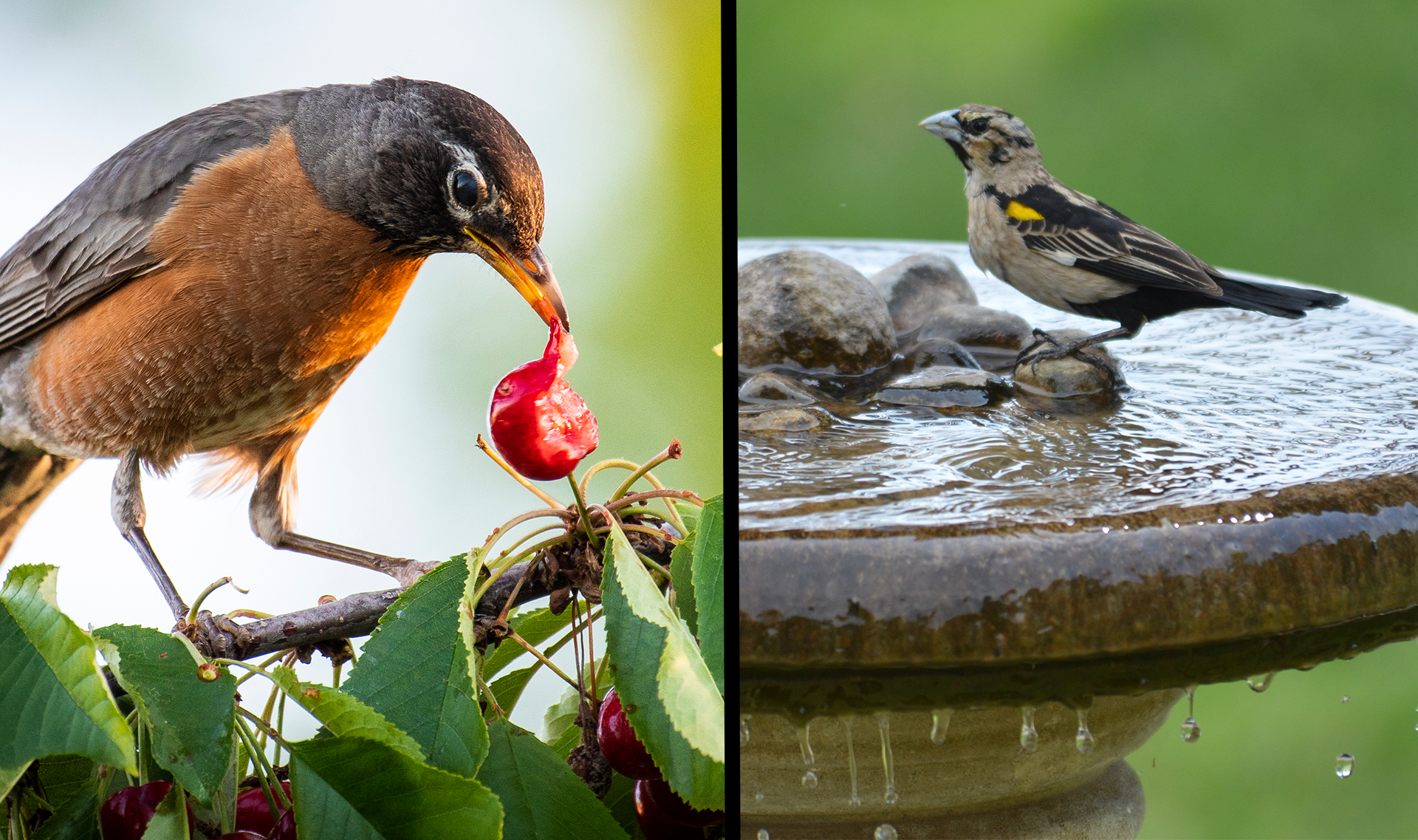

needs
5 of 13
something an animal or plant must have in order to live
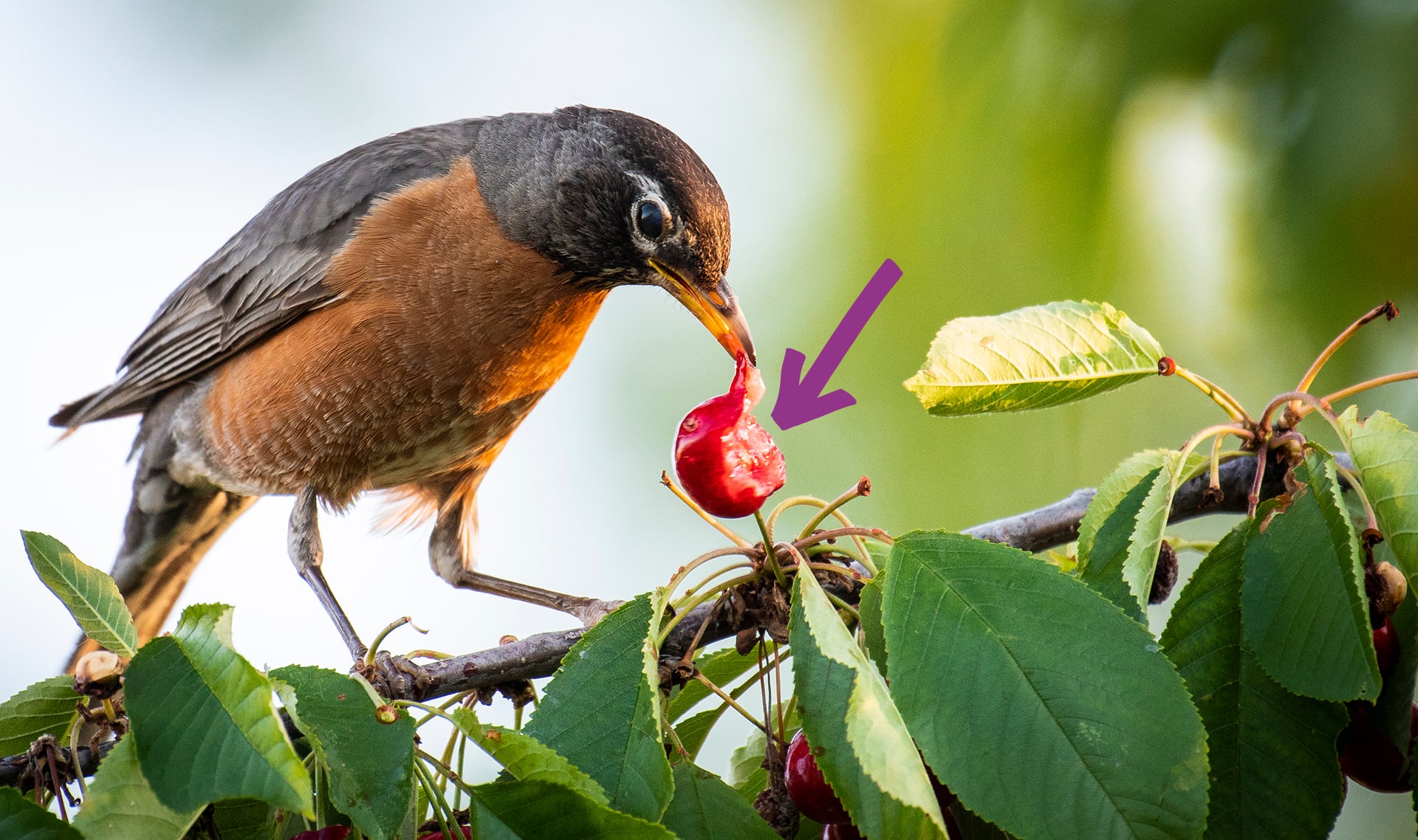

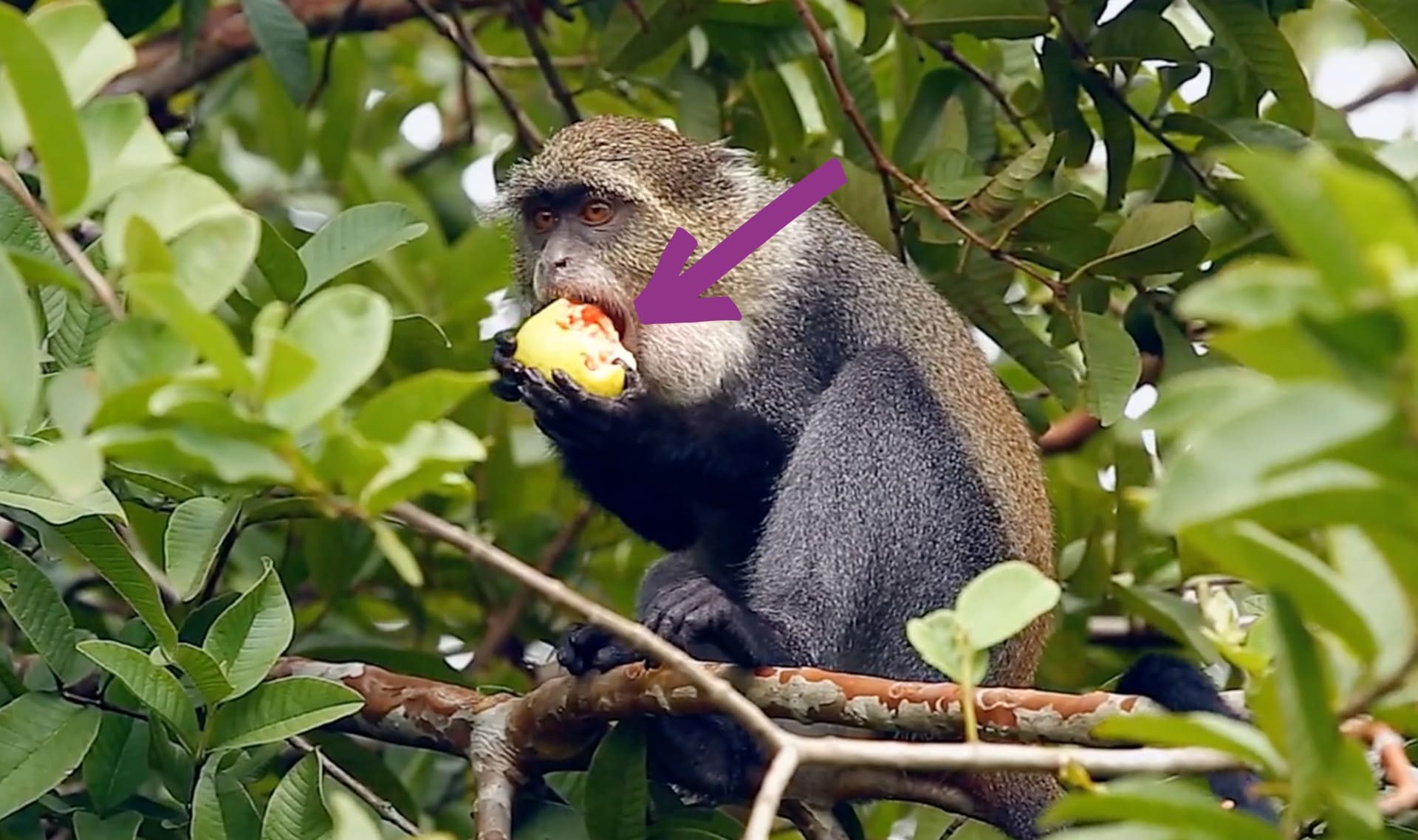
food
6 of 13
something that animals eat

beak
7 of 13
the part of a bird that it uses to eat

mouth
8 of 13
the opening animals use to take in food and water
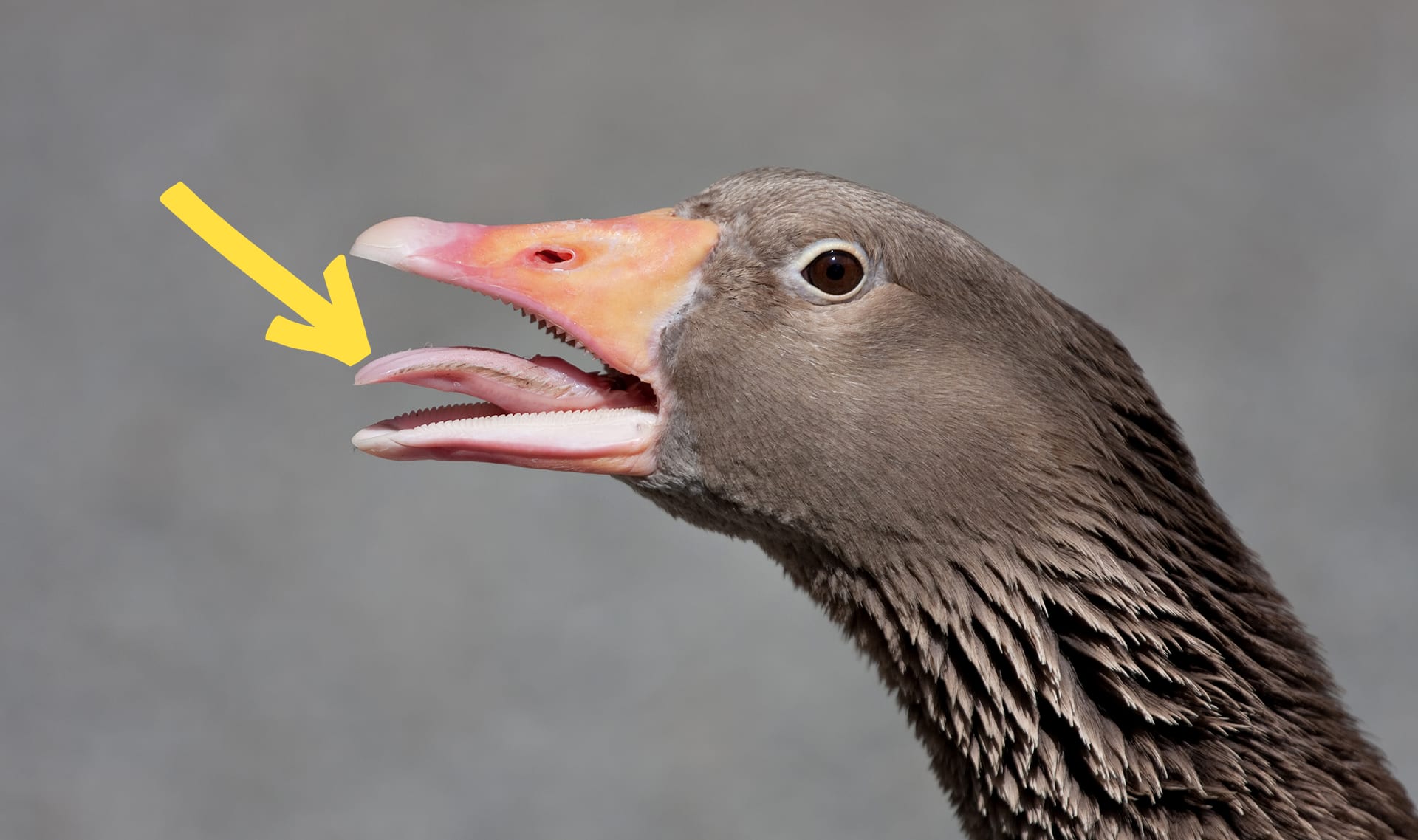
tongue
9 of 13
a part of the body, inside the mouth, used for taste

stomach
10 of 13
a part of the body where food goes after being eaten

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.
survive
11 of 13
to stay alive
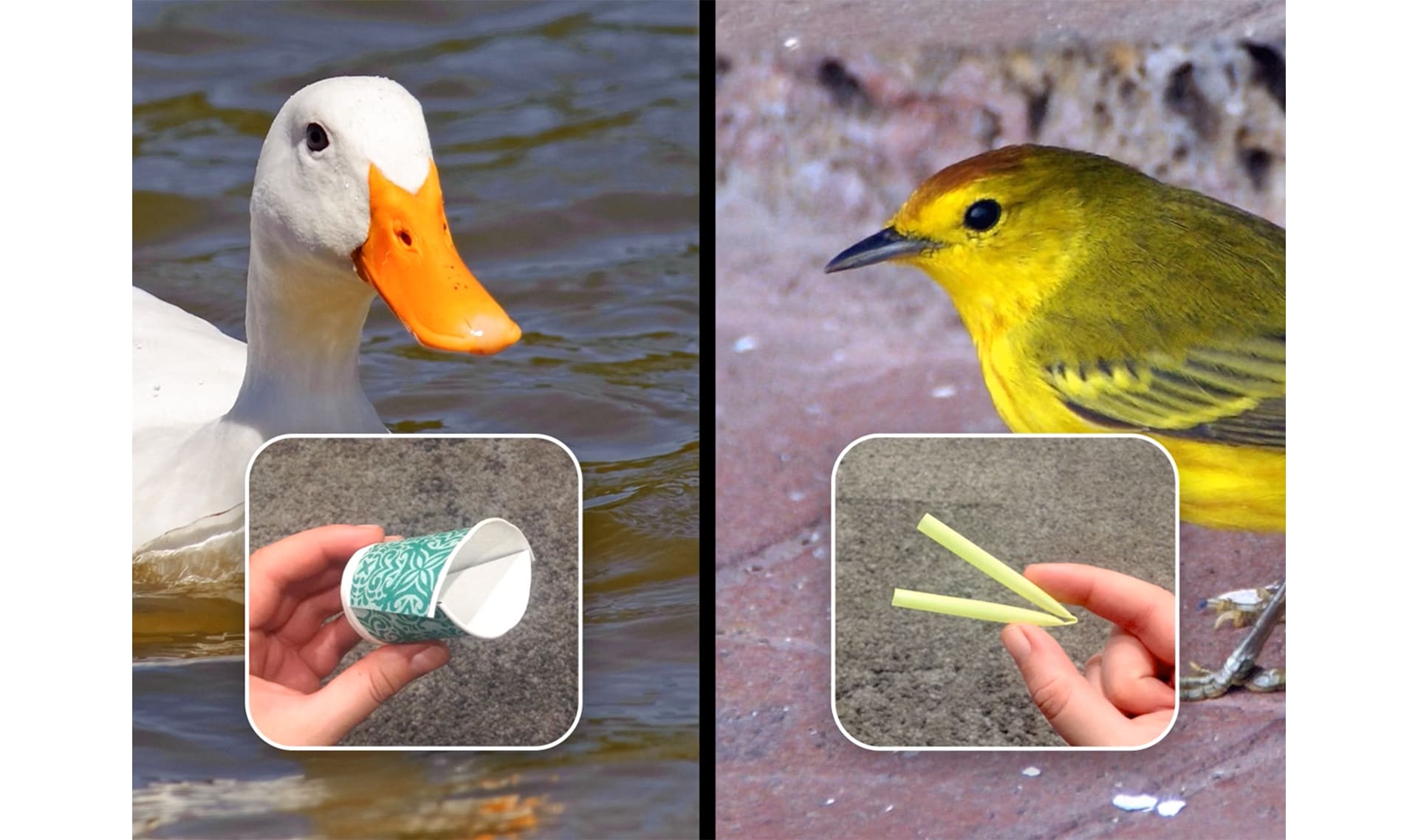

model
12 of 13
a pretend version of something that scientists use when the real thing is too big, small, or complicated to work with

Please wait…
This video is having trouble loading. You may have lost your Internet connection.
Step 1: Click to Reload this page
Step 2: Click to
Try our other video player
Step 3: Contact your teacher if trouble persists.
Or,
dismiss this message.
experiment
13 of 13
a test used to discover new information about a question







